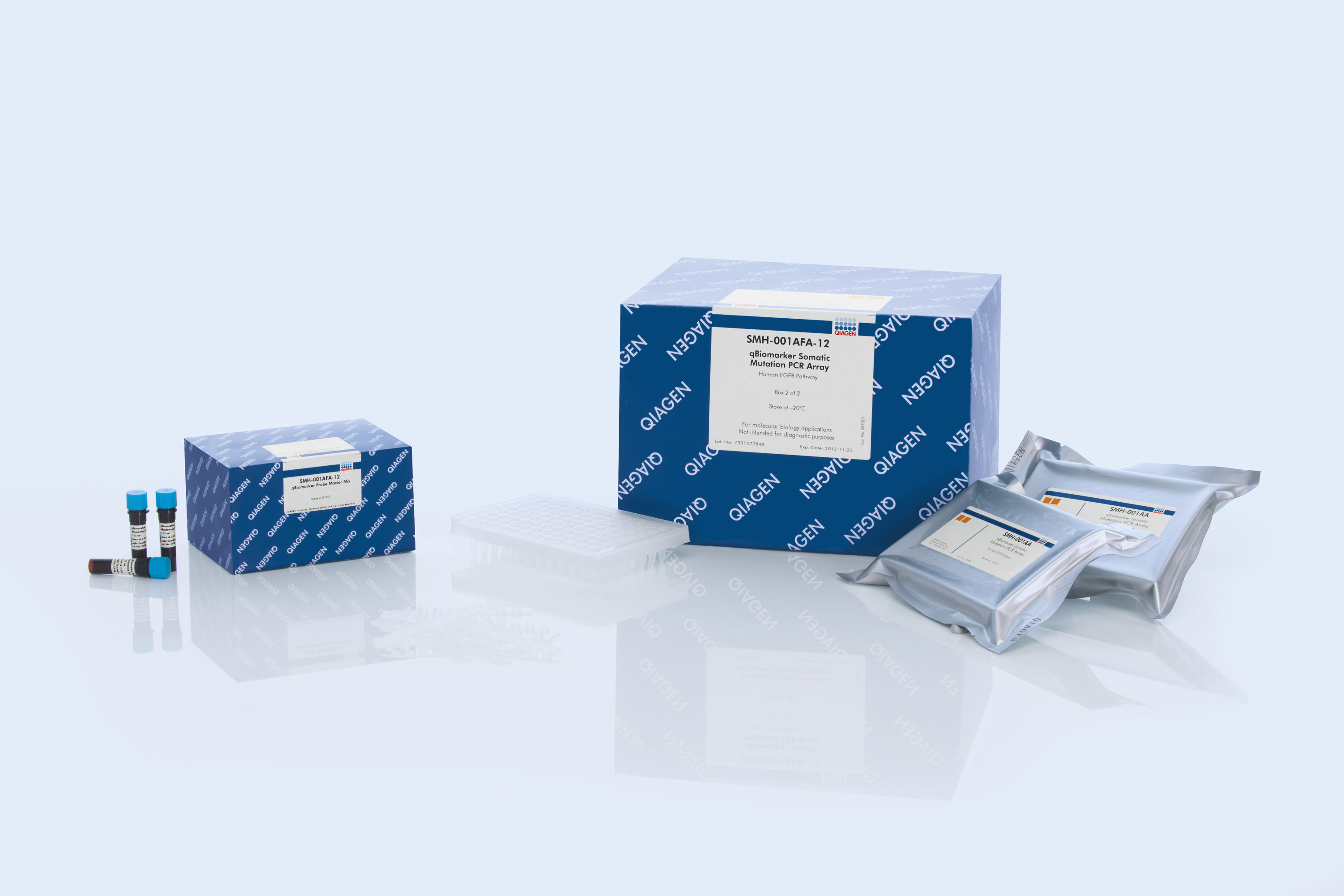
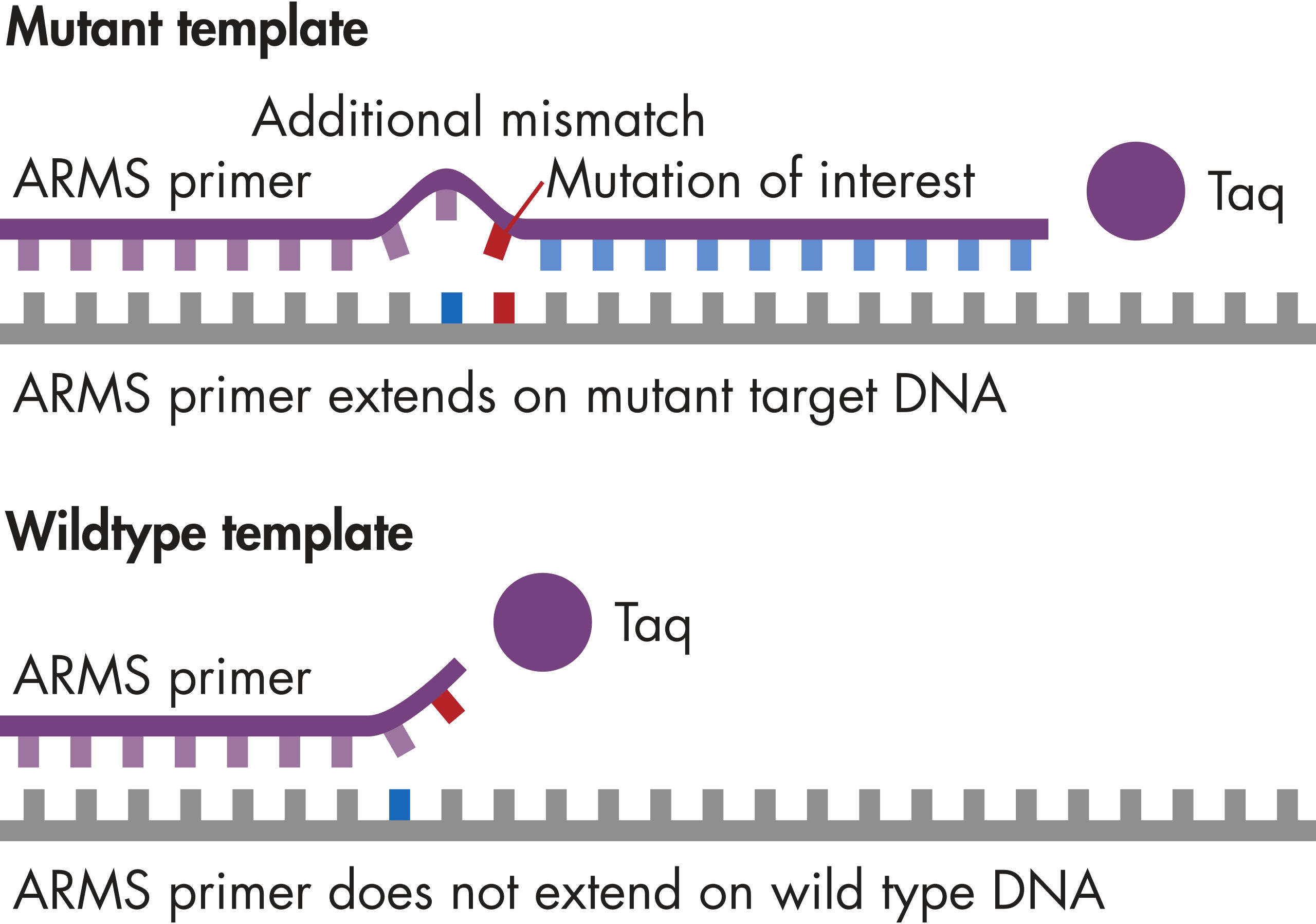
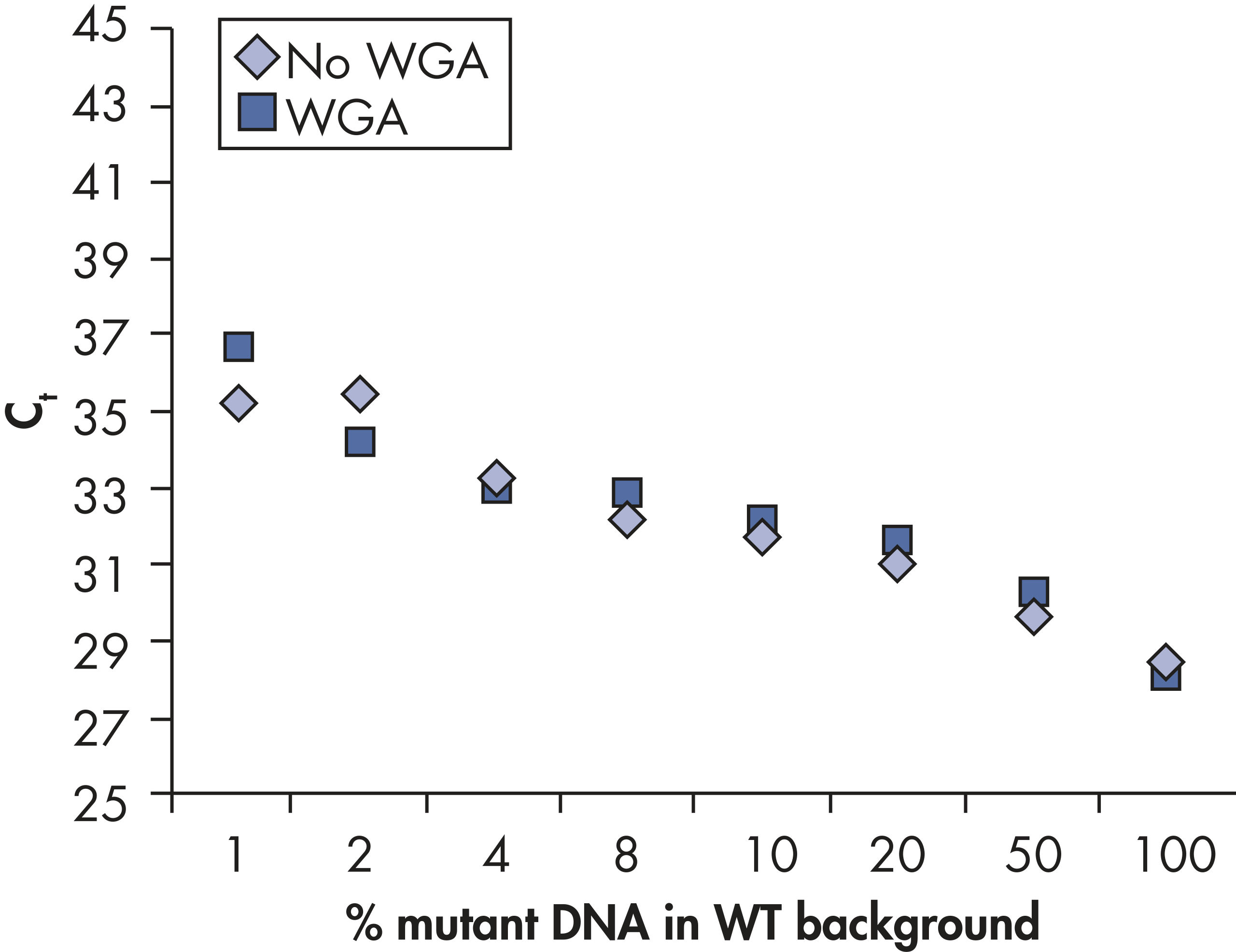
PCR plate and master mix
Target List
ABL1
The mutations queried by these assays mostly lie in the protein kinase domain.
ATM
The most commonly detected ATM loss-of-function mutations occur in the FAT, FATC and kinase domains.
BRAF
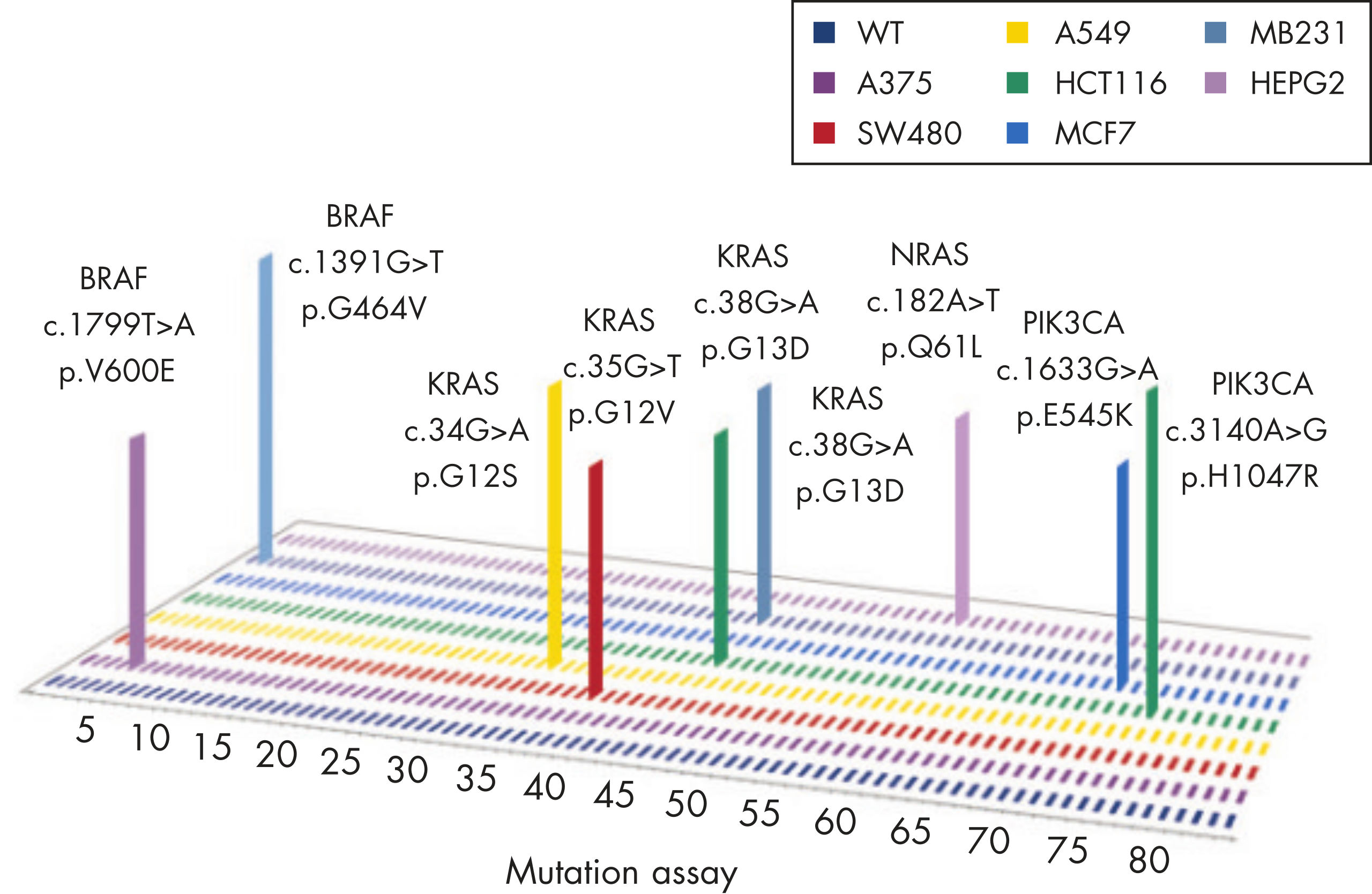
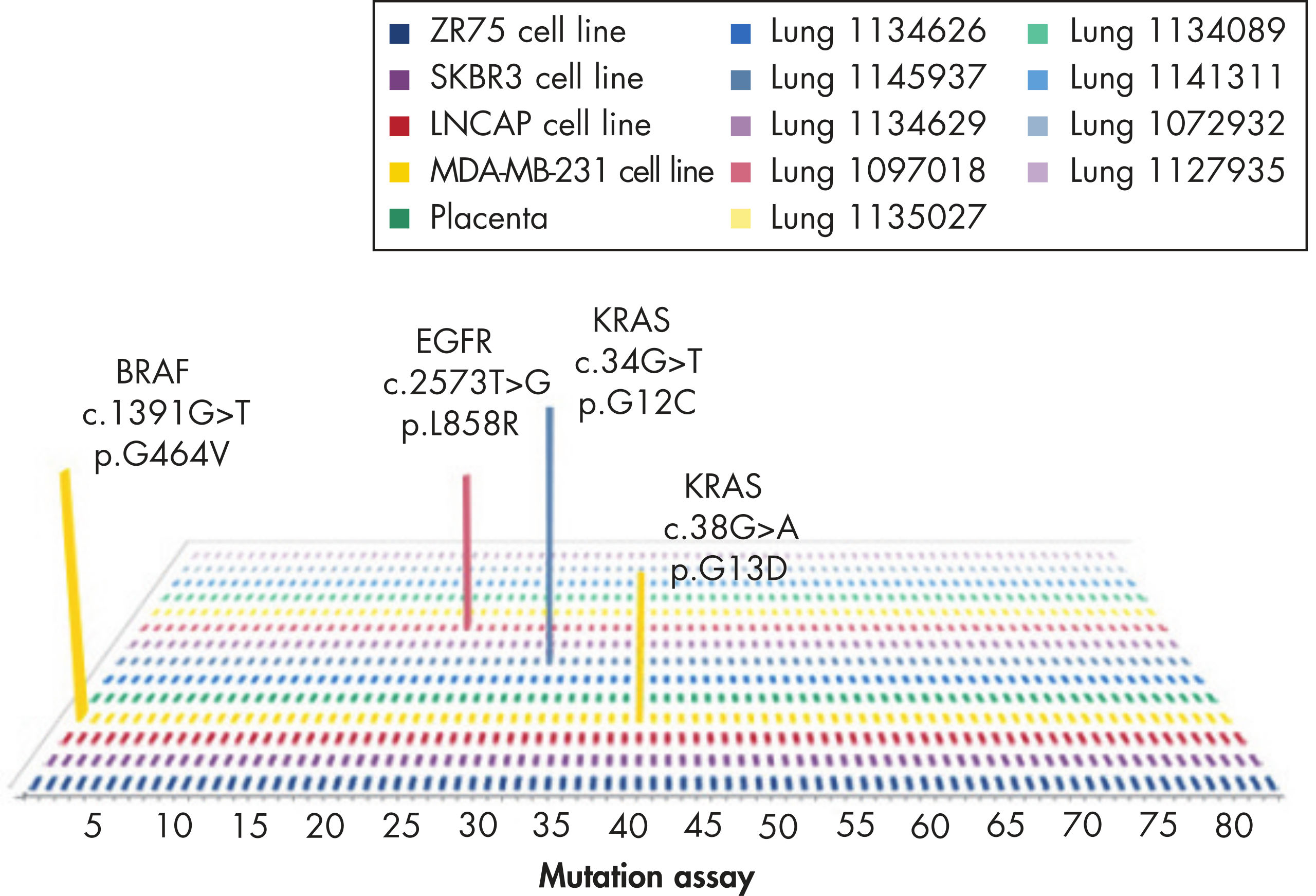
Common point mutations in BRAF either increase kinase activity, such as L597V, L597Q and V600E, or inhibit kinase activity, such as G464V, G466V and G469A.
CDKN2A
The most important CDKN2A loss-of-function mutations occur in the consensus ankyrin domain, which lead to the inability to form stable complexes with its targets.
CRLF2
This novel gain-of-function mutation synergizes with JAK2 R683 mutations to confer cytokine-independent growth to BaF3 pro-B cells.
CTNNB1
The most frequently detected CTNNB1 mutations result in abnormal WNT signaling activity. The mutated codons are mainly several serines and threonines targeted for phosphorylation by GSK3B.
EZH2
All detected mutations lie in the SET domain responsible for histone lysine methyltransferase activity.
FBXW7
These mutation assays detect FBXW7 variants in either the third or the fourth repeat of the protein's WD40 domain, which is involved in protein-protein interactions.
FGFR3
The most frequently identified FGFR mutations occur in their kinase domains and non-kinase extracellular domains such as the hinge regions and IgG-like domains. Some of the somatic mutations also correspond to congenital SNPs involved in genetic diseases.
FLT3
The most frequently identified FLT3 variants include point mutations, insertions and deletions in the juxtamembrane and activation loop domains of the protein.
HRAS
The mutation assays detect the most important HRAS variants, all found in codons 12, 13, and 61.
JAK2
Most of these mutations lie in protein kinase domain 1. One mutation (p.V615F) confers cytokine-independent growth to BaF3 pro-B cells. Mutations at R683 lead to constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation activity promoting cytokine hypersensitivity and are associated with susceptibility to Budd-Chiari syndrome.
KIT
The most frequently identified KIT gain-of-function mutations include the D816V point mutation; point mutations in, and a deletion of, exon 11 (the juxtamembrane domain); an exon 9 insertion; as well as exon 13 point mutations.
KRAS
The mutation assays detect the most frequently occurring KRAS mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61. Mutations at these positions reduce the protein’s intrinsic GTPase activity and/or cause it to become unresponsive to RasGAP.
NOTCH1
Most of the represented mutations lie in the NOTCH1 protein's predicted cytoplasmic domains.
NRAS
The mutation assays detect the most important NRAS variants, all found in codons 12, 13, and 61.
PIK3CA
The most frequently detected PIK3CA gain-of-function mutations occur either in the kinase domain (T1025-G1049, such as H1047L and H1047R) that increase its activity or in the helical domain (P539-E545) which mimic activation by growth factors.
PTPN11
The most frequently identified PTPN11 variants include mutations in or near the N-terminal SH2 domain and PTP-interacting surface as well as mutations that affect substrate specificity.
TP53
The most frequently detected somatic TP53 mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain which disrupt DNA binding and/or protein structure.