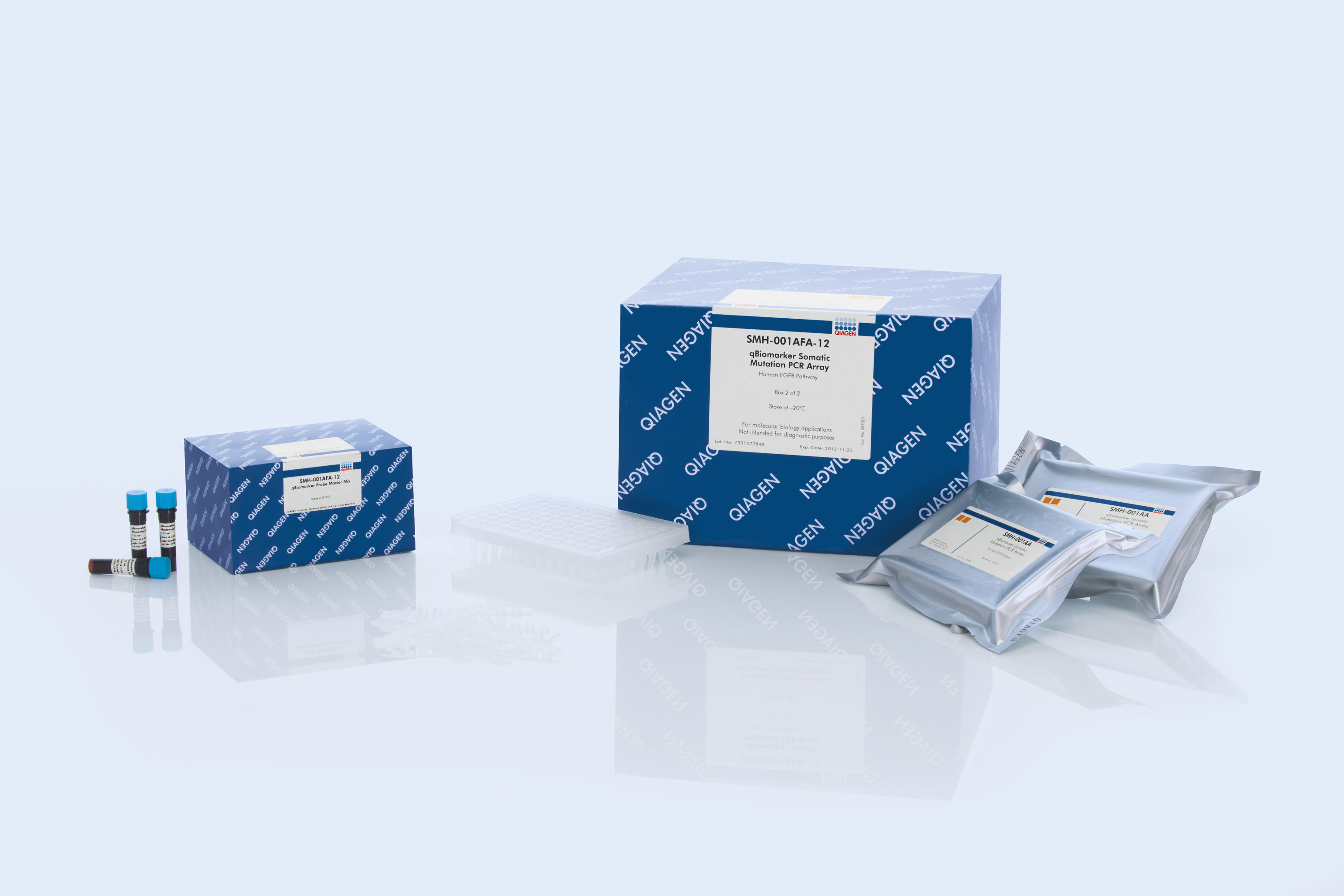
PCR plate and master mix
Target List
AMER1
The mutation assays target two FAM123B (AMER1) nonsense mutations at codons 210 and 358.
ARID1A
The mutation assay targets the ARID1A point mutation A1413V.
CTNNB1
The most frequently detected CTNNB1 mutations result in abnormal WNT signaling activity. The mutated codons are mainly several serines and threonines targeted for phosphorylation by GSK3B.
GNAS
Mutations in this gene result in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a (PHP1a), which has an atypical autosomal dominant inheritance pattern requiring maternal transmission for full penetrance.
KRAS
The mutation assays detect the most frequently occurring KRAS mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61. Mutations at these positions reduce the protein’s intrinsic GTPase activity and/or cause it to become unresponsive to RasGAP.
MET
The most frequently identified MET gain-of-function point mutations lie in its tyrosine kinase and juxtamembrane domains.
MTOR
The most frequently observed MTOR gain-of-function variants occur in its protein's kinase domains and result in constitutive mTOR signaling activation even during nutrient starvation.
PIK3CA
The most frequently detected PIK3CA gain-of-function mutations occur either in the kinase domain (T1025-G1049, such as H1047L and H1047R) that increase its activity or in the helical domain (P539-E545) which mimic activation by growth factors.
TP53
The most frequently detected somatic TP53 mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain which disrupt DNA binding and/or protein structure.
VHL
Included on the panel are 6 of the most commonly detected VHL point mutations or truncation mutations that lead to loss of tumor suppressor function of the VHL protein.
WT1
The WT1 transcription factor plays an essential role in normal urogenital system development. A small subset of patients with Wilm's tumors contains mutations in this gene.